By default, SSH listens on port 22. Changing the default SSH port adds an extra layer of security to your server by reducing the risk of automated attacks.
This tutorial explains how to change the default SSH port in Linux. We will also show you how to configure your firewall to allow access to the new SSH port.
Changing the SSH Port
Changing the SSH port of an image is a simple task. All you need to do is to edit the SSH configuration file and restart the service.
The following sections explain how to change the SSH Port on a Linux system.
Step 1
Choosing a New Port Number
In Linux, port numbers below 1024 are reserved for well-known services and can only be bound to by root. Although you can use a port within a 1-1024 range for the SSH service to avoid issues with port allocation in the future, it is recommended to choose a port above 1026.
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
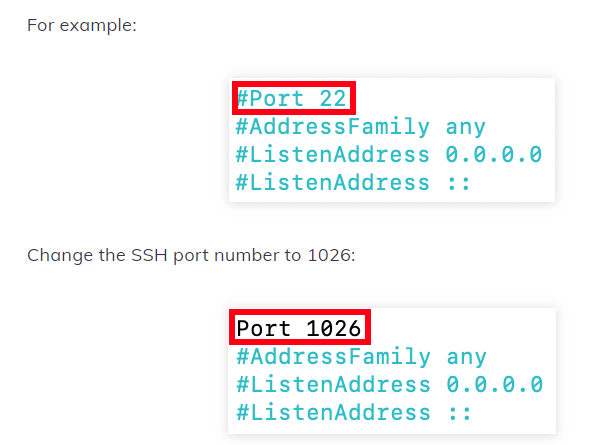
The SSH configuration file will open. Find the line that reads #Port 22. Next, delete the number and # and replace it with the new SSH port number you want to use.
For example:
Step 2
Adjusting Firewall
Before changing the SSH port, you’ll need to adjust your firewall to allow traffic on the new SSH port. For this page, we wil guide you how to change new ssh port from 22 to 1026. Port 1026 can be customized under your own management.
If you are using UFW, the default firewall configuration tool for Ubuntu, run the following command to open the new SSH port:
yum -y install policycoreutils-python
sudo ufw allow 1026 /tcp
In CentOS, the default firewall management tool is FirewallD. To open the new port run:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=1026 /tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
CentOS users also need to adjust the SELinux rules:
sudo semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 1026
If you are using iptables as your firewall, to open the new port, run:
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 1026 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPTStep 3
Configuring SSH
Open the SSH configuration file /etc/ssh/sshd_config with your text editor:
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_configBe extra careful when modifying the SSH configuration file. The incorrect configuration may cause the SSH service to fail to start.
Once done, save the file and restart the SSH service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart ssh
In CentOS the ssh service is named sshd:
sudo systemctl restart sshdIn Debian and Ubuntu, type:
service ssh restart
The output should look something like this:
tcp LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:1026 0.0.0.0:* tcp ESTAB 0 0 192.168.121.108:1026 192.168.121.1:57638 tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::]:4632 [::]:*
Using the New SSH Port
To specify the port, invoke the ssh a command followed by the -p <port_number> option:
ssh -p 1026 username@remote_host_or_ip
If you are regularly connecting to multiple systems, you can simplify your workflow by defining all of your connections in the SSH config file.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned how to change the SSH port on a Linux server. You should also set up an SSH key-based authentication and connect to your Linux servers without entering a password.

